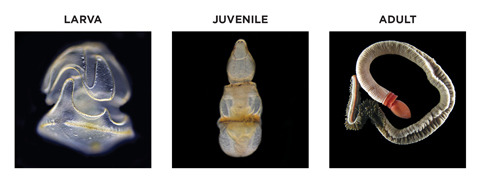
It doesn’t take long for this marine worm to get a head in life—a body, however, is another question. That’s an unexpected insight from Stanford researchers, who, armed with wet suits and shovels, headed to California’s Morro Bay in search of a rare type of acorn worm.
Their study sheds light on indirect developers—animals that transform after a larval stage, like the acorn worm, and which are far less understood than species that essentially begin life as mini-adults.
The researchers found that an acorn worm spends months as little more than a swimming head before it develops a body, which may grow longer than 15 inches. The findings suggest that many ocean animals may share this trunkless stage, reflecting the biological development of early animals.
“Indirect development is the most prevalent developmental strategy of marine invertebrates and life evolved in the ocean,” says Chris Lowe, senior author of the paper and associate professor of biology. “This means the earliest animals probably used these kinds of strategies to develop into adults.”